
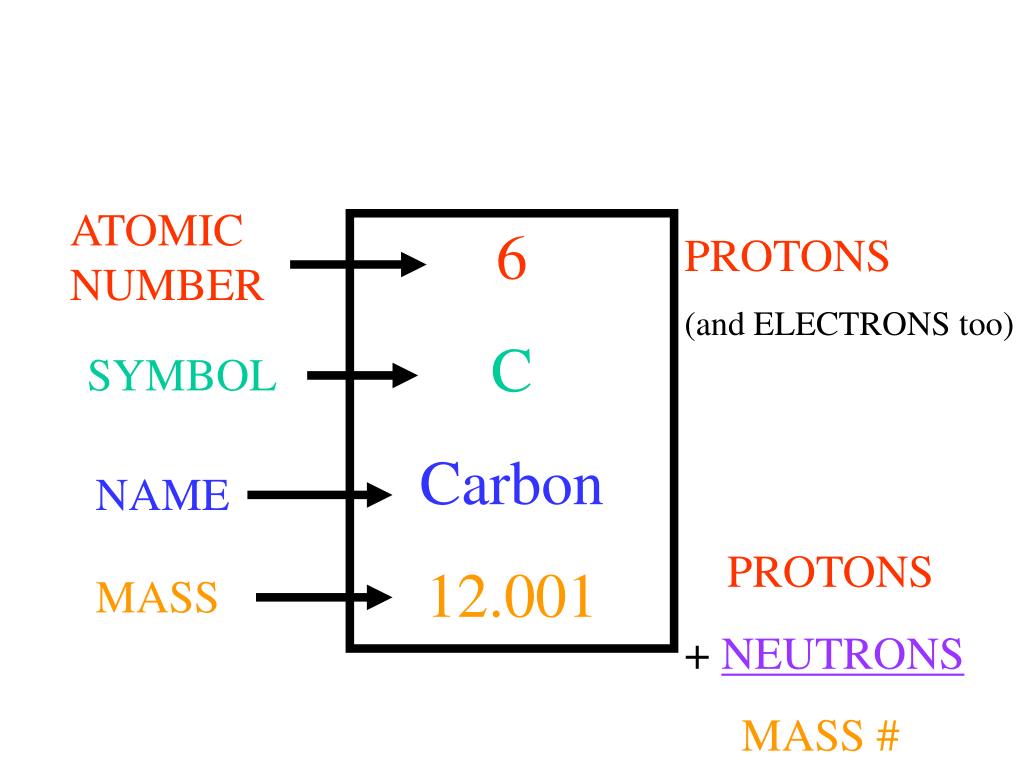
A-level Chemistry/OCR/Atoms, Bonds and Groups/Atoms and Reactions/Atoms.License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks.

Sunil Kumar Singh, Fundamental Force Types.License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlikeĬC LICENSED CONTENT, SPECIFIC ATTRIBUTION The atoms having the same atomic number but different mass number are called Isotopes. For example, a lithium atom (Z=3, A=7 amu) contains three protons (found from Z), three electrons (as the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom), and four neutrons (7 – 3 = 4). The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present). Atomic Number, Isotopes and Isobars - Atomic number of an element is the total number of protons present in that element, Mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons of that element. Given an atomic number (Z) and mass number (A), you can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a neutral atom.

For example, the atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) is 35.45 amu because chlorine is composed of several isotopes, some (the majority) with an atomic mass of 35 amu (17 protons and 18 neutrons) and some with an atomic mass of 37 amu (17 protons and 20 neutrons). Often, the resulting number contains a decimal. Scientists determine the atomic mass by calculating the mean of the mass numbers for its naturally-occurring isotopes. Here are facts about this important and interesting element. This nonmetallic element is the key to the chemistry of living organisms, primarily due to its tetravalent state, which allows it to form four covalent chemical bonds with other atoms. Isotopes of the same element will have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.Ītomic number, chemical symbol, and mass number: Carbon has an atomic number of six, and two stable isotopes with mass numbers of twelve and thirteen, respectively. Carbon is the element with atomic number 6 on the periodic table with symbol C. Protons and neutrons both weigh about one atomic mass unit or amu. This approximation of mass can be used to easily calculate how many neutrons an element has by simply subtracting the number of protons from the mass number. The small contribution of mass from electrons is disregarded in calculating the mass number. \( \newcommand\)Īn element’s mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons. When an organism dies, it stops taking in carbon-14, so the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in its remains, such as fossilized bones, will decline as carbon-14 decays gradually to nitrogen-14 2 ^2 2 squared. As animals eat the plants, or eat other animals that ate plants, the concentrations of carbon-14 in their bodies will also match the atmospheric concentration. As plants pull carbon dioxide from the air to make sugars, the relative amount of carbon-14 in their tissues will be equal to the concentration of carbon-14 in the atmosphere. These forms of carbon are found in the atmosphere in relatively constant proportions, with carbon-12 as the major form at about 99%, carbon-13 as a minor form at about 1%, and carbon-14 present only in tiny amounts 1 ^1 1 start superscript, 1, end superscript.
For example, carbon is normally present in the atmosphere in the form of gases like carbon dioxide, and it exists in three isotopic forms: carbon-12 and carbon-13, which are stable, and carbon-14, which is radioactive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
